#su access linux
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
¿Qué Distribución de Linux Deberías Usar Según tus Intereses? / Which Linux Distribution Should You Use Based on Your Interests?
Introducción / Introduction
Español: Linux ofrece una vasta gama de distribuciones, cada una diseñada para diferentes intereses y necesidades. Ya sea que te enfoques en el desarrollo de software, la administración de sistemas, la creación de contenido multimedia, o simplemente busques una alternativa a Windows o macOS, hay una distribución de Linux que se adapta a ti. Además, Linux proporciona ventajas significativas sobre otros sistemas operativos en muchos de estos escenarios. En este blog, exploraremos cuál distribución es ideal según tus intereses y las razones por las que Linux puede ser una mejor opción en comparación con Windows o macOS. Presentaremos esta información de manera accesible para tanto hispanohablantes como angloparlantes.
English: Linux offers a wide range of distributions, each designed for different interests and needs. Whether you focus on software development, system administration, multimedia creation, or simply seek an alternative to Windows or macOS, there’s a Linux distribution that suits you. Additionally, Linux offers significant advantages over other operating systems in many of these scenarios. In this blog, we’ll explore which distribution is ideal based on your interests and why Linux might be a better choice compared to Windows or macOS. This information will be presented in a way that is accessible to both Spanish and English speakers.
1. Ubuntu: Ideal para Principiantes, Desarrollo y Diseño Gráfico / Ubuntu: Ideal for Beginners, Development, and Graphic Design
Español: Ubuntu es la elección perfecta para quienes son nuevos en Linux o buscan una distribución estable y fácil de usar para el desarrollo de software. Su amplia compatibilidad con aplicaciones como GIMP, Inkscape y Blender también la convierte en una excelente opción para diseñadores gráficos e ilustradores. Además, Ubuntu ofrece soporte para una variedad de herramientas de desarrollo, lo que la hace ideal para programadores.
English: Ubuntu is the perfect choice for those new to Linux or looking for a stable and user-friendly distribution for software development. Its broad compatibility with applications like GIMP, Inkscape, and Blender also makes it an excellent choice for graphic designers and illustrators. Additionally, Ubuntu offers support for a variety of development tools, making it ideal for programmers.
2. Fedora: Para Desarrolladores, Seguridad y Creación de Contenido Multimedia / Fedora: For Developers, Security, and Multimedia Creation
Español: Fedora se destaca por estar a la vanguardia en términos de tecnología y seguridad. Es una distribución ideal para desarrolladores y aquellos interesados en seguridad informática. Además, Fedora es compatible con una amplia gama de software para edición de video, audio y animación, como Kdenlive, Audacity y Blender, lo que la convierte en una opción sólida para creadores de contenido multimedia.
English: Fedora stands out for being at the forefront of technology and security. It’s an ideal distribution for developers and those interested in cybersecurity. Additionally, Fedora supports a wide range of software for video editing, audio production, and animation, such as Kdenlive, Audacity, and Blender, making it a solid choice for multimedia content creators.
3. Debian: Para Administradores de Sistemas, Usuarios Avanzados y Diseño 3D / Debian: For System Administrators, Advanced Users, and 3D Design
Español: Debian es conocida por su estabilidad, lo que la hace ideal para administradores de sistemas y usuarios avanzados. Su entorno sólido también es adecuado para diseñadores 3D que buscan un sistema confiable para trabajar con software como Blender o FreeCAD. Debian proporciona un entorno de trabajo predecible y seguro, ideal para manejar proyectos de gran escala y complejidad.
English: Debian is known for its stability, making it ideal for system administrators and advanced users. Its solid environment is also suitable for 3D designers looking for a reliable system to work with software like Blender or FreeCAD. Debian provides a predictable and secure work environment, ideal for handling large-scale and complex projects.
4. Arch Linux: Para Usuarios Avanzados, Personalización Extrema y Jugadores / Arch Linux: For Advanced Users, Extreme Customization, and Gamers
Español: Arch Linux es la distribución preferida por aquellos que desean un control total sobre su sistema. Es ideal para usuarios avanzados que buscan personalización extrema y desean optimizar su sistema para el rendimiento en juegos. Arch te permite configurar tu entorno de juego con precisión, optimizando el rendimiento con herramientas como Steam y Proton para jugar títulos de Windows en Linux.
English: Arch Linux is the preferred distribution for those who want full control over their system. It’s ideal for advanced users seeking extreme customization and who want to optimize their system for gaming performance. Arch allows you to finely tune your gaming environment, optimizing performance with tools like Steam and Proton for playing Windows titles on Linux.
5. Linux Mint: Alternativa a Windows para Escritorio y Creadores de Contenido / Linux Mint: Windows Alternative for Desktop Users and Content Creators
Español: Linux Mint ofrece una experiencia de usuario familiar para aquellos que buscan una alternativa a Windows, siendo particularmente amigable para el uso en escritorios. También es una excelente opción para creadores de contenido que necesitan una distribución simple y efectiva para trabajar con herramientas como OBS Studio, GIMP y Audacity. Mint combina facilidad de uso con estabilidad, facilitando la transición desde Windows.
English: Linux Mint offers a familiar user experience for those seeking an alternative to Windows, being particularly user-friendly for desktop use. It’s also an excellent choice for content creators who need a simple and effective distribution for working with tools like OBS Studio, GIMP, and Audacity. Mint combines ease of use with stability, making the transition from Windows smooth.
6. Pop!_OS: Para Desarrolladores, Gamers y Diseño 3D / Pop!_OS: For Developers, Gamers, and 3D Design
Español: Pop!_OS es una distribución basada en Ubuntu, optimizada para desarrolladores y jugadores. Incluye soporte nativo para GPUs, lo que la hace ideal para jugar y trabajar en proyectos de diseño 3D con software como Blender. Además, su enfoque en la productividad y el flujo de trabajo eficiente la convierte en una excelente opción para desarrolladores que buscan un entorno de trabajo optimizado.
English: Pop!_OS is a Ubuntu-based distribution optimized for developers and gamers. It includes native GPU support, making it ideal for gaming and working on 3D design projects with software like Blender. Additionally, its focus on productivity and efficient workflow makes it an excellent choice for developers looking for an optimized work environment.
Ventajas de Linux Sobre Windows y macOS / Advantages of Linux Over Windows and macOS
Español: Linux ofrece diversas ventajas sobre Windows y macOS, incluyendo:
Costo: La mayoría de las distribuciones de Linux son gratuitas, lo que reduce significativamente el costo en comparación con las licencias de Windows o macOS.
Seguridad: Linux es conocido por su robusta seguridad, con menos vulnerabilidades a malware debido a su arquitectura y modelo de permisos.
Rendimiento: Linux es más eficiente en el uso de recursos, ofreciendo mejor rendimiento, especialmente en hardware más antiguo o limitado.
Personalización: Con Linux, tienes un control total sobre tu sistema, permitiendo ajustar cada aspecto según tus necesidades, lo que es ideal para usuarios avanzados y creadores de contenido.
English: Linux offers several advantages over Windows and macOS, including:
Cost: Most Linux distributions are free, significantly reducing costs compared to Windows or macOS licenses.
Security: Linux is known for its robust security, with fewer vulnerabilities to malware due to its architecture and permission model.
Performance: Linux is more resource-efficient, offering better performance, especially on older or limited hardware.
Customization: With Linux, you have full control over your system, allowing you to tweak every aspect to fit your needs, ideal for advanced users and content creators.
Conclusión / Conclusion
Español: Elegir la distribución de Linux adecuada puede mejorar significativamente tu experiencia, dependiendo de tus intereses y necesidades. Desde Ubuntu y Fedora para principiantes y desarrolladores, hasta Arch Linux para usuarios avanzados y jugadores, y Pop!_OS para creadores de contenido y diseño 3D, hay una distribución que se adapta a cada perfil. Linux ofrece notables ventajas sobre Windows y macOS, convirtiéndose en una opción atractiva para una amplia variedad de usuarios.
English: Choosing the right Linux distribution can significantly enhance your experience, depending on your interests and needs. From Ubuntu and Fedora for beginners and developers, to Arch Linux for advanced users and gamers, and Pop!_OS for content creators and 3D design, there’s a distribution that fits every profile. Linux offers notable advantages over Windows and macOS, making it an attractive option for a wide range of users.
#Linux#DistribucionesLinux#Ubuntu#Fedora#Debian#ArchLinux#LinuxMint#PopOS#AlternativaWindows#SistemaOperativo#PersonalizaciónLinux#VentajasLinux#LinuxVsWindows#LinuxVsMac#DesarrolloSoftware#AdministraciónSistemas#SeguridadLinux#RendimientoLinux#DiseñoGráfico#Videojuegos#Animación#Diseño3D#CreaciónDeContenido#Ilustración#Multimedia
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Guía de Informática -Grado 10
Hola chicos, subo la con la información de la clase.
Fecha: marzo 18 de 2024
Tema:
Reto Integrador: 1. Evidenciar una página web interactiva y temática con contenido multimedia (según las indicaciones dadas previamente en sala)
2. Crear una campaña sobre “Las Herramientas TIC y su importancia” infórmese y elabore la actividad en su página
Entrega: ____10 de ___ abril de 2024 (cualquier duda, consultar con su docente a tiempo, no el día que debe entregar)
Reto: Escoja uno de los siguientes sitios para elaborar su sitio web
•
WIX
• BLOGSPOT O BLOGGER
• TUMBLR
• WEBNODE
• WEEBLY
• WORDPRESS
• MÉDIUM
• OTROS
Si ya tiene uno, súbale contenido temático (temático significa que sea netamente académico enfocado a TECNOLOGIA E INFORMATICA).
En su blog deben ir apareciendo semana a semana sus informes sobre la evidencia final
-Videos de la elaboración de su evidencia final (mientras realizan la actividad usted puede grabar y/o tomar fotos para ir evidenciando su proceso.
Nota: Cualquier duda, inquietud comunicármela a tiempo. Quedo pendiente
*************
-Programas operativos y aplicativos
Desde la perspectiva de la informática, un programa de aplicación consiste en una clase de software que se diseña con el fin de que para el usuario sea más sencilla la realización de un determinado trabajo. Esta particularidad lo distingue del resto de los programas, entre los cuales se pueden citar a los sistemas operativos.
-Los sistemas operativos son los que permiten el funcionamiento de la computadora, existen varios, tales como (Microsoft Windows - Mac OS X - GNU/Linux – UNIX – Solaris – FreeBSD - OpenBSD: Sistema operativo libre, - Google Chrome OS - Debian – Ubuntu – Mandriva – Sabayon – Fedora - Linpus Linux - Haiku (BeOS)
- Lenguajes de programación (aquellos que dan las herramientas necesarias para desarrollar los programas informáticos en general) y las utilidades (pensadas para realizar acciones de mantenimiento y tareas generales). Tales como (Java - C.- Python.- C++ - C# - Visual Basic. - JavaScript. – Php – Swift – SQL
El software es el elemento intangible y lógico que forma parte de una computadora. Es decir (Los programas se presentan como herramientas para mejorar tu desempeño. Algunos ejemplos de estos programas o aplicaciones son los procesadores de texto, como Microsoft Word; las hojas de cálculo, como Excel; y las bases de datos, como Microsoft Access.)
El hardware, en cambio, es el componente material y físico. Se dice que los sistemas operativos constituyen el lazo que une al software con el hardware.
En ocasiones, los programas de aplicación son diseñados a medida, es decir, según las necesidades y pretensiones de cada usuario. Por eso, el software permite resolver dificultades específicas. En otros casos, se trata de paquetes integrados que solucionan problemas generales e incluyen múltiples aplicaciones. Por ejemplo, un paquete de oficina combina aplicaciones como procesadores de textos y hojas de cálculo.
10. Herramientas para crear maquetas de interfaz de usuario en aplicaciones de software
Balsamiq Mockups. Balsamiq Mockups es una aplicación es muy divertida y sencilla de usar.
Mockingbird.
Mockup Builder.
MockFlow.
HotGloo.
Invision.
JustProto.
Proto.io.
Framer
Origami Studios
InVision
Reto autónomo: Elabore una presentación en PowerPoint o video explicativo, sobre los programas operativos y aplicativos para el manejo de registros, textos, diagramas, figuras, planos constructivos, maquetas, modelos y prototipos con herramientas informáticas.
INFORME FINAL
El docente explica a sus estudiantes como elaborar su informe final, con enlaces directos a las actividades solicitadas durante el periodo.
Nota: También dejo la guía para descarga
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
September 30 2024 2009
Sufficiently quenched theres only one thing left for the cans of Tab.
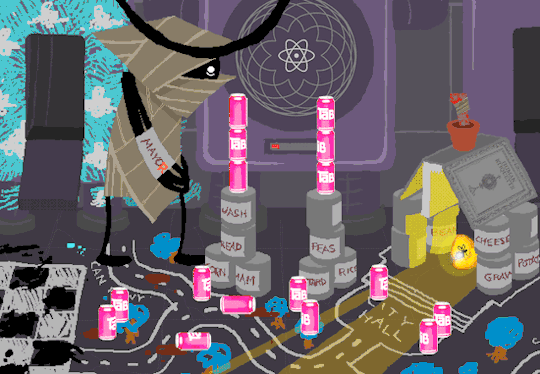
Joining democratic society.
Anyway, WV goes to take a look at the big computer and preses ESCAPE bringing us to a command line screen filled with prompts. At the absolute top are prompts in green that were entered some time before WV appeared.
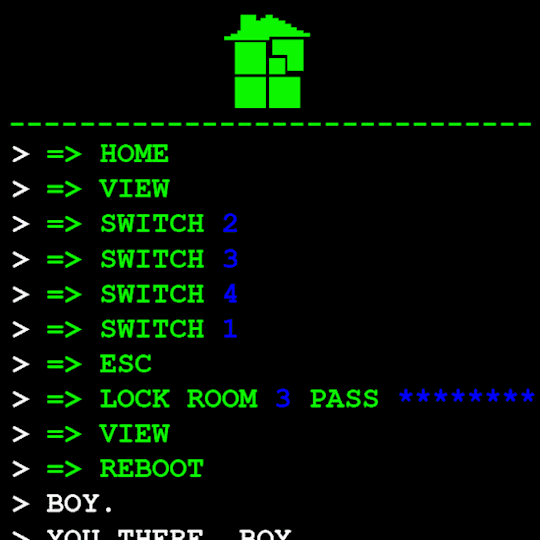
Gonna have to brush off my CS cap for this one. Now since we dont know what system this computer runs on Im going to operate on the assumption that this is Linux as Ive played around more with that terminal than Windows.
I assume that the green text is a Super User (or using sudo privileges but Im pretty sure its rhe former). What is a super user you ask? The windows equivilent would be Admin and essentially gives this user root directory privileges to access the whole system and make changes. Obviously this can lead to problems if done incorrectly so a password is put in place to prevent just anyone from making system changes. Thats where sudo comes in. Sudo elevates the commands you are giving and will require a password when you access.
Now that thats cleared up, lets look at the prompts. Each of these is preceeded with =>, possibly denoting root prompts from a sudo user. Skipping HOME for a moment, we see VIEW which takes us out of the command terminal to video feed on each of the four screens. SWITCH, well, switches between the screens, the order of which was 2-3-4-1.
I dont know if there is a meaning behind starting at two, Roses screen, but screen 2 shows feed of her house displaying static in front of Zazzerpan whos hand has been broken. Screen 3 shows a, to us, future scene of Dave, potentially post strife, and a first level prototyped kernel. This screen brings a lot of questions. Who is Daves server player? If each of these screens is showing current live feed, how much time passed between the strife and prototyping? What happened to Rose that her feed is locked on Zazzerpan? Unfortunately, WV abandons continuing the previous users commands and enters HOME so we cant see who is on screen 4.
Before diving into what happens with the HOME command, lets go back to the green text. ESC we established brings us back to the teminal. Here this user entered the password to LOCK room 3. Its unclear what room 3 is but Im guessing this was supposed to block access to interacting with Dave. Most likely our SU was preparing this computer for whoever stumbled upon it and blocked access to all but Johns screen.
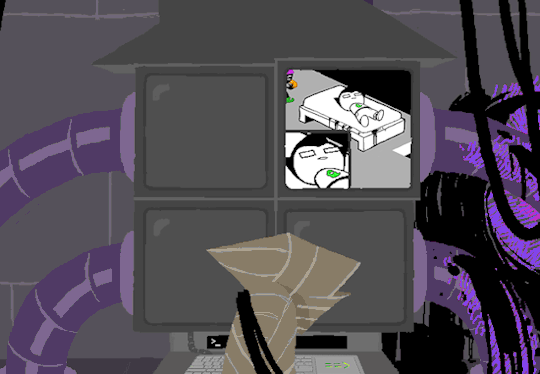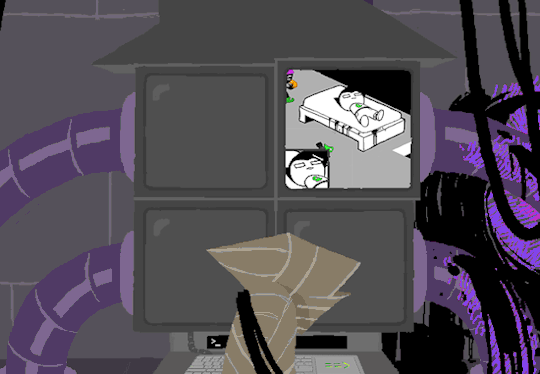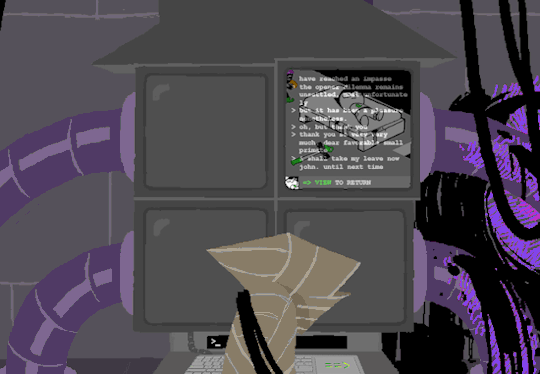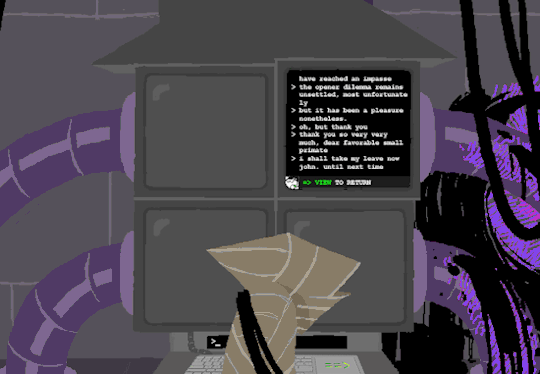
At the bottom of the terminal is a smaller screen that displays the character of focus, in this case John, and the command VIEW which would maximize the camera screen one again. So after ensuring the screens SU wanted were locked, SU returned the view to screen 1 which is what WV saw upon booting. After everything was in order, the system was then rebooted which saved these changes and returned the system to normal user function logging out of the root directory.
In normal user function, entering HOME activates all the screens and our favorite ominous number appears.
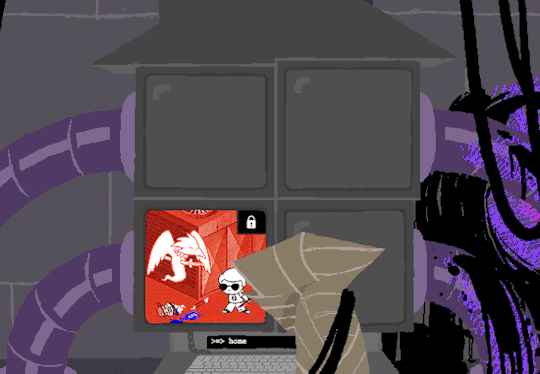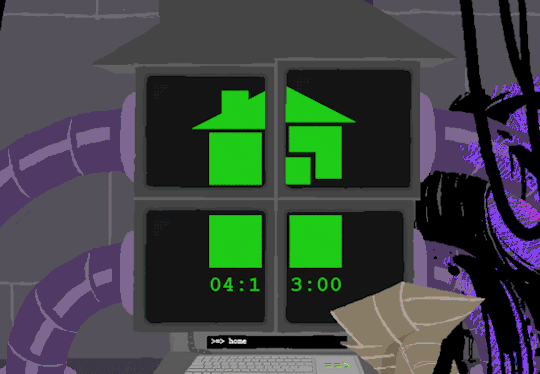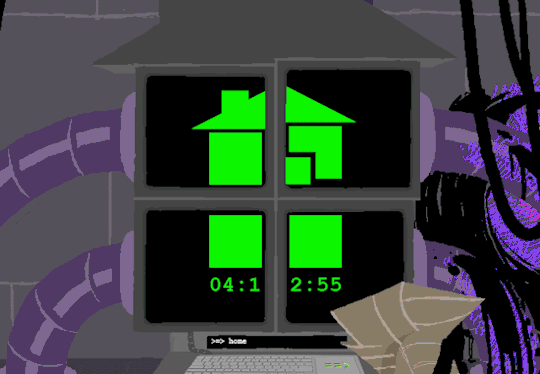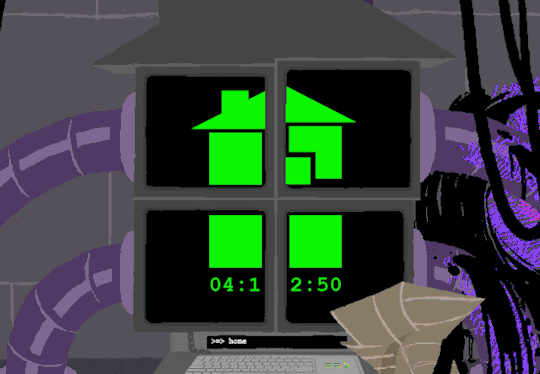
Four hours and thirteen minutes. Another countdown, and this time who knows what its for. Nothing more can be typed as the keyboard is now locked.
But WV is none too worried. He is a Mayor now with much more pressing matters.

The militia wont train itself you know.
#i have an AS in comp sci and a BBA in information systems#all to say i know COMPUTERS for BUSINESS with extra focus on COMPUTERS#this was fun to write#i love sharing knowledge#homestuck#homestuck replay#hsrp liveblog#chrono
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Boost Your Big Data Skills: Hadoop Installation on Ubuntu

Ubuntu blog
Ubuntu is a very powerful Linux-based operating system that is famous for its stability, security, and user-friendliness. Regardless of whether you are a beginner or advanced, Ubuntu will grant you a smooth experience in the world of personal computing, development, and even playing. Being updated regularly with an overreaching robust community, Ubuntu remains growing and more popular among users worldwide.
The first reason why people prefer Ubuntu is flexibility. This means it runs on everything from very low-cost machines to top of the line servers: this is a good fit for all sorts of use cases. If you would like to run a game or some resource-heavy application, Gaming RDP on Ubuntu can provide you with the means to do so seamlessly. The users could easily access their machines with remote desktop protocols and run their favorite games without worrying about hardware limitations. Ubuntu offers multiple gaming client platforms, including Steam, to ensure that users have access to an entire spectrum of games.
To install Hadoop on Ubuntu, follow these steps:
Requirements for Hadoop Installation on Ubuntu
Hadoop Installation
To install Hadoop on Ubuntu, install Java, set up passwordless SSH, download Hadoop, configure environment variables (HADOOP_HOME), format the HDFS namenode, and start Hadoop's services using start-dfs.sh and start-yarn.sh.
Steps 1 : Prepare Your Environment:
To prepare Ubuntu, update packages, install essential tools, configure settings, and set up development or system-specific requirements.
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
Steps 2 : Install Java
To install Java on Ubuntu
sudo apt update
then sudo apt install
default-jdk,
verify with java -
version.ll default-jdk
Steps 3: Create a Hadoop User: ...
This sets up the Hadoop user. You can now install and configure Hadoop as needed.
Create a Hadoop user
Now, the hadoop user is created and ready for setting up Hadoop-related tasks.
To set up SSH key-based authentication for a user on Ubuntu, follow these steps:
1. Generate SSH Key Pair on Local Machine
2. Copy Public Key to Remote Machine
3. Verify Key-Based Authentication
4. Optional: Disable Password Authentication
1. Install Java
Hadoop requires Java to run. If you haven't installed Java, you can install it using the following command:
bash
Copy code
sudo apt update
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk
Check Java version to verify the installation:
bash
Copy code
java -version
2. Create a Hadoop User (Optional)
Create a dedicated Hadoop user (if you haven’t already):
bash
Copy code
sudo useradd -m -s /bin/bash hadoop
sudo passwd hadoop
Switch to the hadoop user:
bash
Copy code
su - hadoop
3. Download Hadoop
Go to the Apache Hadoop releases page and copy the link for the latest stable version. Alternatively, you can download Hadoop using wget:
bash
Copy code
wget https://downloads.apache.org/hadoop/common/stable/hadoop-x.y.z.tar.gz
Replace x.y.z with the version number you want to download.
4. Extract Hadoop Files
Extract the downloaded tarball:
bash
Copy code
tar -xzvf hadoop-x.y.z.tar.gz
Move it to /usr/local/hadoop (or another directory if you prefer):
bash
Copy code
sudo mv hadoop-x.y.z /usr/local/hadoop
5. Set Up Hadoop Environment Variables
Edit the .bashrc file to include Hadoop environment variables:
bash
Copy code
nano ~/.bashrc
Add the following lines at the end of the file:
bash
Copy code
# Hadoop Environment Variables
export HADOOP_HOME=/usr/local/hadoop
export HADOOP_INSTALL=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_COMMON_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_HDFS_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export YARN_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin
export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop
Source the .bashrc file to apply changes:
bash
Copy code
source ~/.bashrc
6. Configure Hadoop
Edit the Hadoop configuration files located in the $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/ directory.
To configure environment variables for Hadoop on Ubuntu, follow these steps:
1. Edit the .bashrc File
The .bashrc file contains environment settings that apply to your user session. Open the .bashrc file for editing:
bash
Copy code
nano ~/.bashrc
2. Add Hadoop Environment Variables
At the end of the .bashrc file, add the following lines to configure Hadoop-related environment variables:
bash
# Hadoop Environment Variables
export HADOOP_HOME=/usr/local/hadoop
export HADOOP_INSTALL=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_COMMON_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_HDFS_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export YARN_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin
export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop
Make sure to replace /usr/local/hadoop with the actual path where you installed Hadoop (if different).
3. Set Java Home
Hadoop requires Java, so you need to define the JAVA_HOME variable. Add the following line (adjust the path if necessary):
bash
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64
This is assuming you are using OpenJDK 8. If you're using a different Java version, adjust the path accordingly.
4. Apply the Changes
After saving the .bashrc file, apply the changes:
bash
Copy code
source ~/.bashrc
5. Verify the Configuration
To ensure that the environment variables are correctly configured, check the variables with the following commands:
You should see the correct Hadoop and Java versions printed on the terminal.
To initialize the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) on your Ubuntu system, follow these steps:
1. Format the Namenode
Before you start HDFS, you need to format the Namenode. This step initializes the HDFS filesystem. You should only do this once after installing Hadoop and setting up the configuration files.
Run the following command to format the Namenode:
bash
Copy code
hdfs namenode -format
This will format the Namenode and prepare HDFS for use. The output should indicate that the format was successful, something like this:
arduino
Copy code
Formatting using sector size 512 bytes.
...
DFS Namenode in safe mode
2. Start HDFS Daemons
Now that the Namenode has been formatted, you need to start the HDFS daemons: the Namenode and Datanode.
Run the following command to start the daemons:
bash
Copy code
start-dfs.sh
This will start both the NameNode and DataNode.
You should see output indicating that the daemons are starting:
bash
Copy code
starting namenode, logging to /usr/local/hadoop/logs/hadoop-hadoop-namenode-<hostname>.log
starting datanode, logging to /usr/local/hadoop/logs/hadoop-hadoop-datanode-<hostname>.log
3. Verify the Daemons Are Running
To check if the HDFS daemons are running correctly, use the jps command to see the list of running Java processes:
bash
Copy code
jps
You should see the following processes:
Example output:
Copy code
12345 NameNode
23456 DataNode
34567 SecondaryNameNode
4. Access the NameNode Web UI
To verify that HDFS is running correctly, you can check the NameNode Web UI. Open a browser and go to:
arduino
Copy code
http://localhost:50070
This page provides information about the HDFS filesystem, including storage usage, active and dead DataNodes, and other useful information.
5. Create Directories in HDFS
Once the HDFS daemons are running, you can start interacting with HDFS. For example, you can create directories in HDFS using the hdfs dfs -mkdir command:
bash
Copy code
hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/hadoop
This will create a directory /user/hadoop in the HDFS filesystem.
6. Verify Directory Creation
To verify that the directory was created successfully, list the contents of the HDFS root directory:
bash
Copy code
hdfs dfs -ls /
You should see the newly created /user/hadoop directory listed.
7. Stop HDFS Daemons
Once you're done working with HDFS, you can stop the HDFS daemons using the following command:
bash
Copy code
stop-dfs.shU
This will stop the NameNode and DataNode daemons.
This source is so friendly, user-friendly, and on community support. It's strong with respect to stability, security, and flexibility for both personal computing and server environments. Ubuntu is based on Linux and is an open-source operating system. It has access to a very big repository of software and tools, all of which install easily through its package manager, APT.
Also, Ubuntu is full of applications compatible with many programs; this will allow you access to streaming services that can be accessed easily. Whether you want to watch movies, play games, or even simply take virtual meetings, Ubuntu provides a whole environment. By using the Linux RDP for remote desktop connection, the user can connect to remote servers or even machines to gain efficient management and support for carrying remote tasks. Besides this, there is also an option of Bluestacks RDP through which you may run any Android application on a remote desktop working as a powerful tool in app testing or development. Being in places such as Germany RDP, this provides remote desktop access in a pretty hassle-free manner and in a more secured high-performance connection. It is a place where a user can access it from virtually anywhere to either work or play. Ubuntu's flexibility makes it usable not only for the geeky developers, enterprises, and casual users.
0 notes
Text
APLICACIONES OFIMÁTICAS LibreOffice
Esta es una suite ofimática gratuita y de un código abierto, que ofrece herramientas similares a las otras suites como Microsoft Office (como. docx, .xlsx, .pptx). Esta es una alternativa popular a las aplicaciones comerciales, dentro de esta aplicación tenemos programas que nos permiten crear y edita diferentes tipos de documentos. LibreOffice es compatible con muchos formatos de archivos, incluidos los de Microsoft Office, lo que esto facilita la apertura y edición de documentos en diferentes plataformas. Es multiplataforma por lo que esto nos puede usarse en varios sistemas operativos como Windows, macOS y Linux.
Writer: Es un procesador de texto similar a Microsoft Word, forma parte de LibreOffice desde su creación en el 2010. Ventajas: Gratuito, código abierto, compatible con múltiples formatos. Desventajas: Interfaz menos intuitiva que Word, menos plantillas. Es un editor de texto avanzado, corrector ortográfico, exportación a PDF
Calc: Hoja de cálculo similar a Microsoft Excel. Su origen es LibreOffice, basado en la suite OpenOffice. Ventajas: Gratuito, soporta funciones avanzadas de hojas de cálculo. Desventajas: menos compatibilidad con macros avanzadas Excel. Análisis de datos, creación de gráficos, soporte para fórmulas complejas.
Impress: Herramienta de presentaciones, similar a PowerPoint. Ventajas: Gratuito, permite exportar a múltiples formatos. Desventajas: Menor calidad de plantillas y efectos de PowerPoint. Creación de presentaciones, compatibilidad con archivos PPT y exportación a Pdf.
Draw: Herramienta de dibujo y diagramas. Ventajas: Funcionalidad avanzadas de diagramación, gratuita. Desventajas: Menos intuitivo que programas de diseño gráfico dedicados. Crear diagramas, flujos de trabajo y dibujos vectoriales .
Bases: Gestor de bases de gestos similar a Microsoft Access. Ventajas: Gratuito, integración con otras bases de datos como MySQL. Desventajas: Menos intuitivo para usuarios sin experiencia. Creación y gestión de bases de datos, soporte para SQL.
Math: Editor de ecuaciones matemáticas. Ventajas: Útil para insertar formulas en documentos, gratuito. Desventajas: Uso limitado fuera de contextos académicos o técnicos. Compatibilidad con Writer e impress.
Este es un proyecto software libre desarrollado por The Document Foundation, una organización sin fines de lucro.
youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
Mixtile Edge 2 Kit– AI based bee detection and tracking
Here I describe usage of Mixtile Edge 2 Kit in agriculture, bee detection, which can be essential for health and survival of bees.

Story

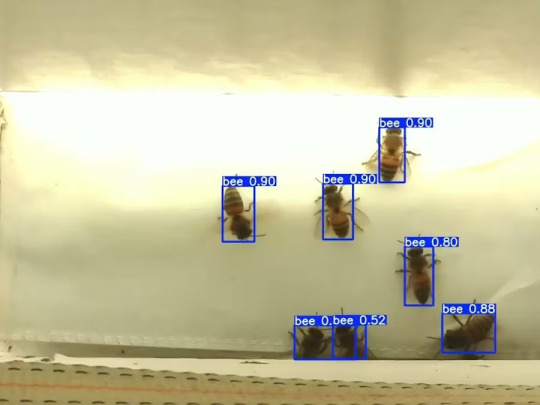
Mixtile is professional IoT hardware solution provider specialized in Linux and Android-based embedded systems.Mixtile Edge 2 Kit is high-performance ARM single board computer. It comes in variants of 2GB of LPDDR4 DRAM and 16GB eMMC Flash storage, or 4GB of LPDDR4 DRAM and 32GB eMMC Flash storage. This single board computer comes with preinstalled Android 11, and it runs Ubuntu Linux operating system in Android container. It comes with large connectivity options (Bluetooth, 4G/5G Cellular, GPS, and Lora, Zigbee and Z-Wave). For those, you will need module, but it comes with default onboard Wi-Fi connectivity, Gigabit Ethernet Port (RJ45) and Serial Port (RS-485). Because it comes with RS-485 port, which is industrial standard, and it comes within a strong metal case, it seems to me that it can be really used in industrial projects. I used official Raspberry Pi 5 power supply in order to power up my Mixtile Edge 2 Kit.So, an idea came to me why not to use it in agriculture, bee detection, which can be essential for health and survival of bees.This project will cover setting up Mixtile Edge 2 Kit, and custom photo dataset form video in order to train custom YOLOv5 bee detection model. YOLOv5 models must be trained on labelled data in order to learn classes of objects in that data.I gathered data from video and trained model on my PC.To train a model, I used python and typed in command line:
python train.py --img 640 --batch 16 --epochs 3 --data coco128.yaml --weights best.pt
My training results are summarized in the following table:
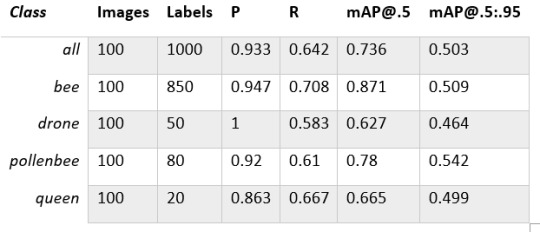
Training results
From this table you can see that images are divided into 4 detection classes:
Bee
Drone
Pollenbee
Queen
Example for each class is summarized in a table below:

Bee classes
1. Getting started
First, I will write about software part of the project, and later on steps of starting the recognition.
1.1 What is YOLOv5?
If you have been in the field of machine learning and deep learning for some time now, there is a high chance that you have already heard about YOLO. YOLO is short for You Only Look Once. It is a family of single-stage deep learning-based object detectors. It was written using Python language, and the framework used is PyTorch.
To ease control, I connected usb mouse to the one of three Mixtile Edge 2 Kit USB3 port. I used Ubuntu Linux for this project. Ubuntu on container is installed in Android system of Mixtile Edge 2 Kit by default. When you boot Mixtile Edge 2 Kit, you get Android OS. Since I wanted to access Edge 2 Kit remotely, and get easier control, I installed droidVNC server from this link:
It is an Android VNC server using Android 5+ APIs. It does not require root access.
I started the VNC server, connected with VNC Viewer and I got the following Android 11 screen:

Android 11
After that, I installed SimpleSSHD from this link:
SimpleSSHD is a SSH server Android app, based on Dropbear.It allows user access (user ssh) or full root access (by setting the login shell to /system/xbin/su) (if root is allowed).
After I installed SSH server, I connected to it via putty SSH terminal. Username and Password are root/root.
Com.hubware.ubuntu is ubuntu on a container and we are connected to it immidiately.
Now we are going to install required software.
First, you will need to upgrade Ubuntu by typing in the command: apt-get upgrade.
Second, I installed python by typing: apt-get install python.
You will also need pip, the package installer for Python.
2. Installing the YOLOv5 Environment
To start off we first clone the YOLOv5 repository and install dependencies. This will set up our programming environment to be ready to running object detection training and inference commands.
Install git: apt-get install git
Clone YOLOv5 repository:
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
Move to YOLOv5 folder:
cd yolov5
Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Wait some time to download and install all requirement packages, I waited 25 minutes, because there are a lot of python packages to install besides YOLOv5. YOLOv5 needs numpy package, scipy, OpenCV, etc.
The putty connection and installation process looks like below:
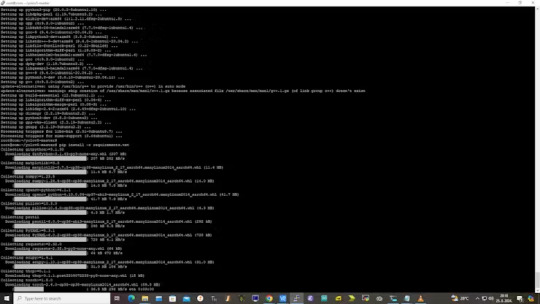
I transferred my model best.pt to the yolov5 installation folder via SCP, with MobaXterm.
You can simply download my model immidiate by typing:
wget https://github.com/sdizdarevic/beedetectionyolov5/raw/main/best.pt
Also, download original video by typing:
wget https://sdizdarevic.typepad.com/cr/bees-orig.mp4
Now, the final step is detection, and we are interested in the “result” content video.
python3 detect.py --weights best.pt --source bees-orig.mp4
The process of detection looks like below:

In the last lines from last picture we can see the detected number of bees at any point in time.
The summarized short steps to follow are below:
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
cd yolov5
pip install -r requirements.txt
wget https://github.com/sdizdarevic/beedetectionyolov5/raw/main/best.pt
wget https://sdizdarevic.typepad.com/cr/bees-orig.mp4
python3 detect.py --weights best.pt --source
Demonstrated videos are on urls with detection finished completely on Mixtile Edge 2 Kit. Output video is in folder runs/detect/exp2.
Original video:
youtube
Result video:
youtube
Last, but not less important: If you want to safely turn off your Mixtile Edge 2 Kit, I recommend you to install Shutdown (no Root) application: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.samiadom.Shutdown&hl=en.
3.Conclusion:
After testing I found out that the Mixtile Edge 2 Kit is designed with wide range of applications, from industrial applications, IOT devices, smart home automation, to more than capable AI and edge detection. It is low powered device, with a lot of built-in connectivity options.
I would like to thank amazing Mixtile people for creating this amazing peace of hardware and especially for sending me the Mixtile Edge 2 Kit. Also, Mixtile nurtures the open source values and software, and I believe more people and companies will be involved in making projects with this board.
All in all, I recommend this board for implementing types of projects I described here.
0 notes
Text
🔒🌍✨ Obtén 3 Meses GRATIS de VPN - Acceso a Internet Seguro y Privado en Todo el Mundo! Haz Clic Aquí ✨🌍🔒
how to use vpn linux
Configuración VPN en Linux
Una VPN, o red privada virtual, es una herramienta crucial para proteger tu privacidad y seguridad en línea. Configurar una VPN en Linux es un proceso relativamente sencillo que te brindará una capa adicional de protección al navegar por internet.
Primero, necesitas elegir un proveedor de VPN confiable que sea compatible con Linux. Algunos de los proveedores más populares ofrecen aplicaciones dedicadas para sistemas Linux, facilitando aún más el proceso de configuración. Una vez que hayas seleccionado tu proveedor, generalmente recibirás instrucciones detalladas sobre cómo configurar la VPN en tu distribución de Linux específica.
La forma más común de configurar una VPN en Linux es a través de la línea de comandos. Puedes utilizar comandos como OpenVPN para establecer la conexión con el servidor VPN de tu elección. Además, muchas distribuciones de Linux vienen preinstaladas con soporte para diferentes protocolos VPN, lo que facilita aún más el proceso de configuración.
Una vez que hayas completado la configuración, podrás disfrutar de una conexión segura y privada en tu sistema Linux. Tu tráfico de internet estará encriptado, lo que significa que tus datos estarán protegidos de posibles ciberataques y miradas no deseadas.
En resumen, configurar una VPN en Linux es una forma efectiva de fortalecer tu seguridad en línea y proteger tu privacidad mientras navegas por internet. No dudes en investigar y elegir el proveedor de VPN adecuado para tus necesidades y seguir las instrucciones proporcionadas para configurar tu VPN con éxito en tu sistema Linux.
Servidores VPN compatibles con Linux
Los servidores VPN son una herramienta crucial en la protección de la privacidad y la seguridad en línea. En el caso de los usuarios de Linux, es fundamental contar con un servidor VPN compatible con este sistema operativo de código abierto.
Afortunadamente, en la actualidad existe una amplia gama de servidores VPN que son totalmente compatibles con Linux. Algunos de los más populares incluyen ExpressVPN, NordVPN, CyberGhost y Private Internet Access. Estos proveedores ofrecen aplicaciones fáciles de instalar y configurar en sistemas Linux, lo que permite a los usuarios proteger sus conexiones de forma rápida y sencilla.
Al elegir un servidor VPN para Linux, es importante tener en cuenta aspectos como la velocidad de conexión, el nivel de seguridad ofrecido y la cantidad de servidores disponibles en diferentes ubicaciones. Además, es fundamental asegurarse de que el proveedor cuente con un sólido servicio de atención al cliente que pueda brindar soporte en caso de surgir algún problema.
En resumen, contar con un servidor VPN compatible con Linux es esencial para garantizar la privacidad y la seguridad en línea. Con las opciones disponibles en el mercado actual, los usuarios de Linux pueden proteger sus datos y navegar por internet de forma segura y anónima.
Herramientas VPN para Linux
Las herramientas VPN para Linux son útiles para aquellos usuarios que desean proteger su privacidad y seguridad en línea mientras utilizan este sistema operativo de código abierto. Una VPN, o red privada virtual, encripta la conexión a Internet del usuario y oculta su dirección IP real, lo que le brinda anonimato y privacidad al navegar por la web.
Existen diversas opciones de herramientas VPN disponibles para usuarios de Linux, tanto gratuitas como de pago. Algunas de las más populares incluyen OpenVPN, WireGuard, SoftEther VPN y NordVPN. Estas herramientas ofrecen diversas funcionalidades, como el acceso a servidores en diferentes ubicaciones geográficas, protocolos de encriptación avanzados y cortafuegos integrados para una mayor protección.
Al utilizar una herramienta VPN en Linux, los usuarios pueden acceder de forma segura a contenido restringido geográficamente, proteger sus datos sensibles en redes Wi-Fi públicas y evitar la censura en línea. Además, las VPN son especialmente útiles para aquellos que desean proteger su privacidad frente a posibles rastreos de gobiernos, proveedores de servicios de Internet u hackers.
En resumen, las herramientas VPN para Linux son una excelente opción para aquellos usuarios que buscan proteger su privacidad y seguridad en línea de forma efectiva y sencilla. Con una amplia variedad de opciones disponibles, es importante elegir la que mejor se adapte a las necesidades y preferencias de cada usuario.
Pasos para usar VPN en Linux
Los VPN, o redes privadas virtuales, son una herramienta útil para proteger tu privacidad en línea y acceder a contenido restringido geográficamente. En Linux, utilizar un VPN es sencillo siguiendo algunos pasos básicos.
El primer paso es elegir un proveedor de VPN confiable y descargar su software compatible con Linux. Una vez descargado, instálalo siguiendo las instrucciones proporcionadas por el proveedor.
Después de instalar el software, inicia sesión con tus credenciales de VPN. A continuación, elige el servidor al que deseas conectarte. Es importante seleccionar un servidor cercano para minimizar la latencia y maximizar la velocidad de conexión.
Una vez conectado al servidor VPN, tu tráfico de Internet estará encriptado y tu dirección IP se ocultará, brindándote anonimato y seguridad en línea. Puedes navegar por la web de forma segura y acceder a contenido restringido geográficamente como si estuvieras en otra ubicación.
Para desconectarte del servidor VPN, simplemente cierra la aplicación o desconéctate manualmente desde la interfaz del software.
En resumen, usar un VPN en Linux es un proceso sencillo que requiere solo unos pocos pasos. Protege tu privacidad en línea y disfruta de una navegación segura y sin restricciones con esta herramienta poderosa.
Seguridad VPN en entorno Linux
La seguridad en línea es de suma importancia en la actualidad, y una forma efectiva de proteger la información confidencial es a través del uso de VPN (Redes Privadas Virtuales). En entornos Linux, la implementación de una VPN garantiza una capa adicional de seguridad para la comunicación y transferencia de datos.
Las VPN en entornos Linux funcionan cifrando la conexión entre el usuario y el servidor, lo que permite ocultar la dirección IP real y encriptar el tráfico de datos. Esto resulta fundamental para proteger la información sensible de posibles ciberataques o vigilancia no autorizada.
Al configurar una VPN en Linux, es importante elegir un protocolo de cifrado seguro, como OpenVPN o IPSec, que garantice la confidencialidad de la información transmitida. Además, se recomienda utilizar contraseñas fuertes y certificados digitales para reforzar la autenticación de los usuarios y los servidores.
Es fundamental mantener actualizados tanto el software de la VPN como del sistema operativo Linux para evitar vulnerabilidades de seguridad. Asimismo, se aconseja limitar el acceso a la VPN solo a usuarios autorizados y monitorear de cerca la actividad en la red para detectar posibles intrusiones.
En resumen, la seguridad de una VPN en entornos Linux es esencial para proteger la privacidad y la integridad de los datos en línea. Al adoptar buenas prácticas de configuración y mantenimiento, se puede garantizar una comunicación segura y confiable en todo momento.
0 notes
Text
how to use vpn on ubuntu
🔒🌍✨ Obtén 3 Meses GRATIS de VPN - Acceso a Internet Seguro y Privado en Todo el Mundo! Haz Clic Aquí ✨🌍🔒
how to use vpn on ubuntu
Configuración VPN en Ubuntu
Una VPN, o red privada virtual, es una herramienta útil para garantizar la privacidad y seguridad en línea al enmascarar tu dirección IP y cifrar tus datos mientras navegas por internet. Configurar una VPN en Ubuntu es un proceso sencillo que te permite proteger tu conexión en tu sistema operativo Linux.
Para configurar una VPN en Ubuntu, primero necesitas elegir un proveedor de servicios VPN confiable y descargar su software o configurar manualmente la conexión. Ubuntu ofrece soporte nativo para los protocolos de VPN más populares, como OpenVPN, PPTP y L2TP.
Una vez que hayas descargado el software o configurado la conexión manualmente, deberás ingresar la información proporcionada por tu proveedor de VPN, como la dirección del servidor, tu nombre de usuario y contraseña.
Después de ingresar la información necesaria, puedes activar la conexión VPN en Ubuntu y comenzar a navegar de forma segura y privada. Recuerda que una VPN no solo protege tu privacidad en línea, sino que también te permite acceder a contenido restringido geográficamente y evitar la censura en internet.
En resumen, configurar una VPN en Ubuntu es una forma eficaz de proteger tu privacidad y seguridad en línea. Sigue los pasos mencionados anteriormente y disfruta de una navegación segura y anónima en tu sistema operativo Linux.
Mejores VPN para Ubuntu
En la actualidad, la seguridad en línea es más importante que nunca, especialmente para los usuarios de Ubuntu. Una forma efectiva de proteger tus datos y privacidad mientras navegas en la web es utilizando una VPN (Red Privada Virtual). Sin embargo, no todas las VPN son compatibles con Ubuntu, por lo que es crucial elegir la correcta. A continuación, te presentamos algunas de las mejores VPN para Ubuntu.
NordVPN: Con servidores en todo el mundo y una sólida política de no guardar registros, NordVPN es una excelente opción para los usuarios de Ubuntu que buscan seguridad y privacidad en línea.
ExpressVPN: Reconocida por su velocidad y facilidad de uso, ExpressVPN es otra VPN premium que ofrece una sólida protección en línea para los usuarios de Ubuntu.
CyberGhost: Ideal para usuarios principiantes, CyberGhost cuenta con una interfaz intuitiva y servidores optimizados para streaming y torrenting.
Private Internet Access (PIA): Con una política estricta de no guardar registros y una amplia gama de servidores, PIA es una opción confiable para proteger tus datos en Ubuntu.
ProtonVPN: Destacando por su enfoque en la privacidad y la seguridad, ProtonVPN ofrece una opción gratuita con límites de velocidad, así como planes premium para una mayor protección.
Al elegir una VPN para Ubuntu, es importante considerar aspectos como la seguridad, la velocidad y la compatibilidad con el sistema operativo. Con estas recomendaciones, podrás navegar de forma segura y proteger tu privacidad en línea mientras utilizas Ubuntu.
Ventajas de usar VPN en Ubuntu
Las VPN (redes privadas virtuales) ofrecen una serie de ventajas cuando se utilizan en sistemas Ubuntu. En primer lugar, la principal ventaja de utilizar una VPN en Ubuntu es la privacidad y seguridad que proporciona. Al conectarse a través de una VPN, todo el tráfico de internet se cifra, lo que garantiza que la información sensible permanezca protegida de posibles ciberataques.
Otra ventaja de utilizar una VPN en Ubuntu es la capacidad de acceder a contenido restringido geográficamente. Al cambiar la dirección IP, es posible simular la ubicación en otro país y así desbloquear sitios web o servicios que de otra manera estarían limitados en ciertas regiones.
Además, las VPN en Ubuntu también ofrecen una capa adicional de anonimato en línea, ya que la dirección IP real del usuario queda oculta. Esto resulta especialmente útil para evitar el rastreo de la actividad en línea por parte de anunciantes u otras entidades.
Por último, al utilizar una VPN en Ubuntu, se puede disfrutar de una mayor velocidad y estabilidad de la conexión, ya que la información viaja a través de servidores dedicados que suelen estar optimizados para ofrecer un rendimiento óptimo.
En resumen, las VPN en Ubuntu ofrecen una serie de ventajas significativas, desde la protección de la privacidad y la seguridad en línea hasta el acceso a contenido restringido y una mejor experiencia de conexión a internet.
Protocolos VPN compatibles con Ubuntu
Los usuarios de Ubuntu a menudo buscan soluciones VPN que sean compatibles con su sistema operativo de código abierto. Afortunadamente, existen diversos protocolos VPN que son compatibles con Ubuntu y que ofrecen una conexión segura y privada para los usuarios.
Uno de los protocolos más populares compatibles con Ubuntu es OpenVPN. Este protocolo de código abierto es altamente configurable y ofrece un alto nivel de seguridad para proteger la información del usuario mientras navega por internet. OpenVPN es compatible con una amplia gama de dispositivos y sistemas operativos, incluido Ubuntu, lo que lo convierte en una excelente opción para los usuarios que buscan una solución VPN confiable.
Otro protocolo VPN compatible con Ubuntu es L2TP/IPsec. Este protocolo es ampliamente compatible con la mayoría de los dispositivos y sistemas operativos, incluido Ubuntu. L2TP/IPsec ofrece un buen equilibrio entre seguridad y velocidad de conexión, lo que lo convierte en una opción popular entre los usuarios de Ubuntu que desean proteger su privacidad en línea.
En resumen, los usuarios de Ubuntu tienen varias opciones de protocolos VPN compatibles que les permiten navegar de forma segura y privada por internet. Tanto OpenVPN como L2TP/IPsec son excelentes opciones para los usuarios de Ubuntu que buscan proteger su información personal mientras utilizan una conexión VPN.
Instalación de cliente VPN en Ubuntu
La instalación de un cliente VPN en Ubuntu es un proceso sencillo que te permitirá proteger tus datos y navegar de forma segura en internet. Un cliente VPN te ayuda a enmascarar tu dirección IP real y encriptar tu conexión, lo que brinda mayor privacidad y seguridad al navegar en línea.
Para instalar un cliente VPN en Ubuntu, primero debes seleccionar un proveedor de servicios de confianza que se ajuste a tus necesidades. Una vez que hayas elegido un servicio, puedes proceder a instalar el cliente VPN siguiendo los pasos proporcionados por el proveedor. Por lo general, esto implica descargar un archivo de configuración específico para Ubuntu y ejecutar algunos comandos en la terminal.
Es importante tener en cuenta que la configuración de un cliente VPN puede variar dependiendo del proveedor de servicios que elijas. Algunos proveedores ofrecen aplicaciones gráficas que facilitan la instalación y configuración del cliente VPN, mientras que otros requieren un enfoque más manual a través de la línea de comandos.
Una vez que hayas instalado con éxito el cliente VPN en tu sistema Ubuntu, podrás conectarte de forma segura a servidores VPN en todo el mundo y disfrutar de una experiencia de navegación más segura y privada. Recuerda mantener tu cliente VPN actualizado y configurarlo según tus preferencias de seguridad para maximizar sus beneficios. ¡Protege tus datos y navega de forma segura con un cliente VPN en Ubuntu!
0 notes
Text
how to find network interface of pia vpn on mac
🔒🌍✨ Obtén 3 Meses GRATIS de VPN - Acceso a Internet Seguro y Privado en Todo el Mundo! Haz Clic Aquí ✨🌍🔒
how to find network interface of pia vpn on mac
Identificar interfaz de red
La interfaz de red es un elemento fundamental en cualquier dispositivo que se conecta a una red, ya sea a través de Wi-Fi, cable Ethernet o tecnologías similares. Identificar la interfaz de red es un paso crucial para asegurarse de que el dispositivo está correctamente conectado y configurado para comunicarse con otros dispositivos en la red.
Para identificar la interfaz de red en un dispositivo, es importante acceder a la configuración de red. En sistemas operativos como Windows, macOS o Linux, esta información suele encontrarse en el panel de control o en la configuración de red.
Una vez en la configuración de red, es posible identificar la interfaz de red por su nombre o dirección MAC. El nombre de la interfaz puede variar según el sistema operativo y el tipo de conexión (Wi-Fi, Ethernet, etc.), por lo que es importante conocer las especificidades de cada dispositivo.
La dirección MAC, por otro lado, es un identificador único asignado a cada interfaz de red. Esta dirección permite distinguir una interfaz de red de las demás y facilita su identificación en entornos de red complejos.
En resumen, identificar la interfaz de red en un dispositivo es esencial para garantizar una conexión de red estable y segura. Conocer el nombre y la dirección MAC de la interfaz facilita la configuración y resolución de problemas en la red, mejorando así la experiencia de conectividad para el usuario.
PIA VPN en Mac
PIA VPN en Mac: Cómo proteger tu privacidad en línea
Utilizar una VPN en tu Mac es una excelente manera de proteger tu privacidad en línea y garantizar una navegación segura. PIA VPN, también conocido como Private Internet Access, es una de las opciones más populares entre los usuarios de Mac debido a su fiabilidad y facilidad de uso.
Con PIA VPN, puedes ocultar tu dirección IP real y encriptar tu conexión, lo que te protege de posibles ciberataques y te permite navegar de forma anónima. Además, PIA VPN cuenta con servidores en todo el mundo, lo que te permite desbloquear contenido restringido geográficamente y acceder a sitios web y servicios que de otra manera no estarían disponibles en tu ubicación.
La configuración de PIA VPN en tu Mac es sencilla y solo toma unos minutos. Una vez instalado el software, puedes elegir entre una variedad de servidores y protocolos para optimizar tu conexión. PIA VPN también ofrece funciones adicionales, como el bloqueo de anuncios y malware, para una experiencia de navegación aún más segura.
En resumen, PIA VPN es una excelente opción para proteger tu privacidad en línea y mantener tu Mac seguro mientras navegas por Internet. Con su combinación de seguridad y facilidad de uso, PIA VPN es una herramienta esencial para cualquier usuario de Mac que valore su privacidad en línea. ¡Protege tu información personal y disfruta de una navegación segura con PIA VPN en tu Mac!
Encontrar interfaz de red
Cuando se trata de encontrar la interfaz de red adecuada para una configuración específica, es fundamental entender cómo identificar y seleccionar la opción correcta. La interfaz de red es el punto de conexión entre un dispositivo y una red, permitiendo la comunicación y transferencia de datos de manera eficiente.
Para encontrar la interfaz de red en un dispositivo, primero debes acceder a la configuración de red. Esto se puede hacer a través del panel de control en sistemas operativos como Windows o MacOS, o mediante comandos en la terminal en sistemas basados en Unix o Linux. Una vez en la configuración de red, podrás ver una lista de interfaces disponibles, que pueden incluir conexiones cableadas como Ethernet o inalámbricas como Wi-Fi.
Es importante tener en cuenta las necesidades específicas de tu red al elegir la interfaz adecuada. Si necesitas una conexión más estable y rápida, es posible que prefieras una conexión Ethernet por cable. Por otro lado, si la movilidad es primordial, una conexión Wi-Fi puede ser más conveniente.
En resumen, encontrar la interfaz de red adecuada implica explorar las opciones disponibles, considerar las necesidades de la red y seleccionar la opción que mejor se adapte a tus requerimientos. Con la interfaz de red correcta, podrás disfrutar de una conexión confiable y eficiente para todas tus actividades en línea.
PIA VPN
PIA VPN, o Private Internet Access, es uno de los proveedores de servicios VPN más populares y confiables en la actualidad. Con una amplia base de usuarios en todo el mundo, PIA VPN se destaca por su enfoque en la privacidad y la seguridad en línea.
Una de las principales características de PIA VPN es su sólida política de no registros, lo que significa que no se almacena ningún dato del usuario, garantizando así la privacidad y el anonimato en línea. Además, PIA VPN utiliza cifrado de nivel militar para proteger la información del usuario, lo que lo convierte en una opción segura para navegar por internet, especialmente en redes públicas.
Otra ventaja de PIA VPN es su velocidad y fiabilidad. Con servidores ubicados en múltiples países, los usuarios pueden disfrutar de una conexión rápida y estable en todo momento, lo que es ideal para actividades como transmitir contenido en línea, descargar archivos y jugar videojuegos.
Además, PIA VPN ofrece una amplia gama de funciones adicionales, como el bloqueo de anuncios y malware, la protección contra fugas de DNS y la posibilidad de conectar hasta 10 dispositivos simultáneamente.
En resumen, PIA VPN es una excelente opción para aquellos que buscan proteger su privacidad en línea, mantenerse seguros en internet y disfrutar de una experiencia de navegación rápida y sin restricciones. Con su enfoque en la seguridad y la privacidad, PIA VPN se posiciona como uno de los mejores proveedores de servicios VPN en el mercado actual.
Mac VPN networking
Un VPN (Red Privada Virtual, por sus siglas en inglés) para Mac es una herramienta cada vez más popular entre los usuarios de Apple que desean proteger su privacidad y seguridad en línea. Al conectarse a un VPN, su tráfico de Internet se cifra y se redirige a través de servidores seguros, lo que impide que terceros accedan a su información personal y actividad en línea.
Al configurar un VPN en su Mac, puede acceder a redes privadas de manera segura, incluso cuando utiliza redes Wi-Fi públicas. Esto resulta especialmente útil para proteger sus datos confidenciales, como contraseñas, información bancaria o archivos importantes. Además, un VPN puede ayudar a evitar la censura en línea y las restricciones geográficas, permitiéndole acceder a contenido bloqueado en su región.
Para configurar un VPN en su Mac, simplemente necesita descargar una aplicación de VPN confiable, crear una cuenta e iniciar sesión. A continuación, podrá elegir entre una variedad de servidores en todo el mundo para una conexión rápida y segura. Algunas opciones populares de VPN para Mac incluyen ExpressVPN, NordVPN y CyberGhost, que ofrecen cifrado sólido, políticas estrictas de no registro y velocidades de conexión rápidas.
En resumen, un VPN para Mac es una herramienta esencial para proteger su privacidad en línea, navegar de manera segura y acceder a contenido restringido. ¡No espere más y mejore su seguridad en Internet con un VPN para Mac hoy mismo!
0 notes
Text
how to install private internet access vpn on kali linux
🔒🌍✨ Obtén 3 Meses GRATIS de VPN - Acceso a Internet Seguro y Privado en Todo el Mundo! Haz Clic Aquí ✨🌍🔒
how to install private internet access vpn on kali linux
Configuración de Private Internet Access en Kali Linux
Private Internet Access es uno de los servicios de VPN más populares y confiables en el mercado. Configurarlo en Kali Linux puede brindarte una capa adicional de privacidad y seguridad al navegar por internet.
Para configurar Private Internet Access en Kali Linux, primero necesitas tener una cuenta activa con ellos. Una vez que hayas creado tu cuenta y te hayas suscrito al servicio, puedes seguir estos pasos para configurarlo en tu sistema:
Descarga el software de Private Internet Access desde su sitio web oficial.
Abre una terminal en Kali Linux e inicia sesión como superusuario.
Navega hasta la ubicación donde descargaste el archivo de instalación y ejecuta el comando para instalarlo.
Una vez que la instalación haya finalizado, ejecuta el comando para iniciar el cliente de Private Internet Access.
Ingresa tus credenciales de inicio de sesión de Private Internet Access para conectarte a sus servidores VPN de forma segura.
Puedes seleccionar manualmente el servidor al que deseas conectarte o dejar que el cliente elija el mejor servidor disponible automáticamente.
Una vez conectado, tu tráfico de internet estará cifrado y tu dirección IP real estará oculta, brindándote anonimato y privacidad mientras navegas por la web.
Configurar Private Internet Access en Kali Linux es una forma efectiva de proteger tu privacidad en línea y mantener seguros tus datos personales. ¡No dudes en probarlo y navegar de forma segura!
Pasos para instalar VPN Private Internet Access en Kali Linux
Para muchos usuarios de Kali Linux, la instalación de un VPN como Private Internet Access es fundamental para proteger su privacidad y seguridad en línea. A continuación, se detallan los pasos para instalar VPN Private Internet Access en Kali Linux:
Paso 1: Lo primero que debes hacer es abrir una terminal en Kali Linux. Puedes hacerlo fácilmente presionando las teclas "Ctrl + Alt + T".
Paso 2: A continuación, debes descargar el instalador de Private Internet Access desde su sitio web oficial. Puedes hacerlo ejecutando el siguiente comando en la terminal: "wget https://www.privateinternetaccess.com/installer/pia-nm.sh".
Paso 3: Una vez descargado el instalador, debes hacerlo ejecutable. Para ello, debes usar el comando: "chmod +x pia-nm.sh".
Paso 4: Luego, procede a ejecutar el instalador con el siguiente comando: "./pia-nm.sh". Esto iniciará el asistente de instalación de Private Internet Access.
Paso 5: Sigue las instrucciones del asistente de instalación para configurar tu cuenta de Private Internet Access y establecer la conexión a través de la VPN.
Paso 6: Una vez completada la instalación, podrás conectarte y desconectarte de Private Internet Access directamente desde el icono de red en la barra de herramientas de Kali Linux.
Siguiendo estos sencillos pasos, podrás instalar y configurar VPN Private Internet Access en Kali Linux de forma rápida y sencilla, protegiendo así tu privacidad y manteniendo tu seguridad en línea. ¡Disfruta de una navegación segura y anónima!
Tutorial para configurar Private Internet Access en Kali Linux
Private Internet Access es una herramienta popular de VPN que ofrece anonimato y privacidad en línea a sus usuarios. Si utilizas Kali Linux y estás buscando cómo configurar Private Internet Access en este sistema operativo, estás en el lugar correcto.
A continuación, te ofrecemos un tutorial sencillo para configurar Private Internet Access en Kali Linux:
Paso 1: Lo primero que necesitas hacer es registrarte en Private Internet Access y obtener tus credenciales de inicio de sesión.
Paso 2: Abre una terminal en Kali Linux y asegúrate de tener instalado el paquete necesario para la conexión VPN. Puedes instalarlo con el comando: sudo apt-get install openvpn network-manager-openvpn network-manager-openvpn-gnome
Paso 3: Descarga el archivo de configuración de Private Internet Access desde su sitio web o solicítalo al soporte técnico.
Paso 4: Abre la terminal nuevamente y navega hasta la ubicación donde guardaste el archivo de configuración. Conéctate al servidor VPN deseado con el comando: sudo openvpn nombrearchivo.ovpn
Paso 5: Ingresa tus credenciales de inicio de sesión cuando se te soliciten y ¡listo! Tu conexión VPN a Private Internet Access debería estar funcionando en Kali Linux.
¡Ahora puedes disfrutar de una conexión segura y privada en tu sistema operativo Kali Linux con Private Internet Access! Recuerda siempre proteger tu privacidad en línea y utilizar una VPN confiable como Private Internet Access.
Procedimiento de instalación de Private Internet Access VPN en Kali Linux
Private Internet Access es una de las VPN más populares y confiables disponibles en el mercado. Si deseas proteger tu privacidad en línea y mantener tus datos seguros mientras usas Kali Linux, instalar Private Internet Access es una excelente opción.
El procedimiento para instalar Private Internet Access VPN en Kali Linux es sencillo y directo. Primero, necesitas descargar el software de la página oficial de Private Internet Access. Una vez descargado, abre una terminal en Kali Linux y navega hasta la carpeta donde guardaste el archivo descargado.
A continuación, descomprime el archivo y ejecuta el instalador. Sigue las instrucciones en pantalla para completar la instalación. Una vez que hayas instalado Private Internet Access, puedes abrir la aplicación y configurar tu cuenta.
Private Internet Access ofrece una amplia gama de servidores en todo el mundo, lo que te permite elegir la ubicación que mejor se adapte a tus necesidades. Además, la VPN utiliza encriptación de grado militar para proteger tus datos y garantizar tu anonimato en línea.
En resumen, instalar Private Internet Access VPN en Kali Linux es una forma efectiva de proteger tu privacidad y seguridad en línea. Sigue los pasos mencionados anteriormente y disfruta de una experiencia en línea más segura y privada.
Guía paso a paso para instalar Private Internet Access en Kali Linux
Para aquellos que desean una mayor privacidad y seguridad en línea al usar Kali Linux, la instalación de Private Internet Access (PIA) es una excelente opción. Este proveedor de servicios VPN ofrece una serie de funciones avanzadas para proteger su conexión a Internet y anonimizar su actividad en línea. A continuación, presentamos una guía paso a paso para instalar PIA en Kali Linux:
Paso 1: Descarga del software Dirígete al sitio web oficial de Private Internet Access y descarga el software para Linux. Asegúrate de seleccionar la versión adecuada para tu sistema operativo.
Paso 2: Instalación del software Una vez descargado el archivo, abre una terminal en Kali Linux y navega hasta la carpeta donde se encuentra el archivo descargado. Ejecuta el comando de instalación para configurar PIA en tu sistema.
Paso 3: Configuración de la cuenta Inicia el software de Private Internet Access y accede con tus credenciales de cuenta. Si aún no tienes una cuenta, regístrate en el sitio web de PIA para obtener un nombre de usuario y una contraseña.
Paso 4: Selección de servidor Una vez que hayas iniciado sesión, selecciona un servidor VPN al que te gustaría conectarte. PIA ofrece una amplia gama de servidores en todo el mundo para una experiencia de navegación segura y rápida.
Con estos sencillos pasos, puedes instalar y configurar Private Internet Access en Kali Linux para proteger tu privacidad en línea y disfrutar de una conexión segura en todo momento. ¡Navega de forma segura y anónima con PIA!
0 notes
Text
Hacks and Anti-Hacks
In order to hack or to prevent hacks, and this is similar to anti-virus software; you need root access to perform both of these effectively.
The problem at that point is that each become indistinguishable from a Virus. Many anti-virus software even have "removal tools" in order to uninstall them completely because they operate in such a fashion.
And this is why we invented "Root" access in the first place. From Linux/Unix OS sudo su. Windows; admin. iOS/android root.
They might also call something like this "Kernel Access".
Now, there are ways to ask Windows to perform an action. A keybind or macro for example; that does not require Kernel access. And there are ways and tool that you can use to inspect memory use and storage without Kernel access.
But most cheat creators don't know how to use those tools despite that being *exactly* what they're doing. Which is kinda strange all things considered.
Typical Anti-Cheat software monitors its own memory usage in order to prevent altercations. And so if something drastically changes or affects the games memory or processes in an abnormal way; will shut the game down and may ban you.
There are many ways to cheat without root access, so this isn't a cover-all. But the more sophisticated hacks, the ones that allow you to manipulate the game's memory and processes *while* it's playing require this access.
And so if you're hacking you're downloading hacks and cheats; you're giving access to developers who aren't above hacking to give themselves an advantage.
You effectively let the hackers have control over your data and computer at the root/Kernel/administrator level.
Good Job.
0 notes
Text
Comparativa de Gestores de Paquetes en Linux: apt vs. dnf vs. pacman / Comparing Package Managers in Linux: apt vs. dnf vs. pacman
Introducción / Introduction
Español: Los gestores de paquetes son una pieza clave en cualquier distribución de Linux, ya que facilitan la instalación, actualización y gestión de software. Tres de los gestores de paquetes más populares son apt (usado en Debian, Ubuntu y derivadas), dnf (utilizado por Fedora y Red Hat), y pacman (nativo de Arch Linux). Cada uno tiene sus particularidades, ventajas y desventajas. En este blog, haremos una comparativa detallada para ayudarte a entender cuál de estos gestores de paquetes podría ser más adecuado para tus necesidades.
English: Package managers are a key component of any Linux distribution, as they facilitate the installation, update, and management of software. Three of the most popular package managers are apt (used in Debian, Ubuntu, and derivatives), dnf (utilized by Fedora and Red Hat), and pacman (native to Arch Linux). Each has its quirks, strengths, and weaknesses. In this blog, we’ll provide a detailed comparison to help you understand which of these package managers might be better suited to your needs.
apt: El Estándar de Debian y Ubuntu / apt: The Debian and Ubuntu Standard
Español: apt es el gestor de paquetes predeterminado en distribuciones basadas en Debian, como Ubuntu, Linux Mint y otros sistemas derivados. Es conocido por su simplicidad y robustez, siendo ideal para usuarios de todos los niveles.
1. Facilidad de Uso: Una de las mayores ventajas de apt es su facilidad de uso. Los comandos básicos como sudo apt update y sudo apt upgrade permiten a los usuarios mantener su sistema actualizado con facilidad. Además, apt es muy intuitivo, lo que lo convierte en una excelente opción para principiantes.
2. Amplia Documentación: Dado que Debian y Ubuntu son algunas de las distribuciones más populares, existe una enorme cantidad de documentación y recursos disponibles para solucionar problemas y aprender a usar apt de manera efectiva. Esto reduce significativamente la curva de aprendizaje y ayuda a resolver problemas rápidamente.
3. Soporte de Paquetes: apt ofrece acceso a una vasta cantidad de paquetes en los repositorios oficiales de Debian y Ubuntu. Además, la compatibilidad con PPA (Personal Package Archives) permite a los usuarios acceder a versiones más recientes de software o a programas que no están en los repositorios oficiales.
Desventajas: Aunque apt es extremadamente fiable, puede ser más lento en comparación con otros gestores de paquetes como pacman, especialmente en sistemas con muchas actualizaciones pendientes.
English: apt is the default package manager in Debian-based distributions such as Ubuntu, Linux Mint, and other derivatives. It’s known for its simplicity and robustness, making it ideal for users of all levels.
1. Ease of Use: One of the biggest advantages of apt is its ease of use. Basic commands like sudo apt update and sudo apt upgrade allow users to keep their system up-to-date with ease. Additionally, apt is very intuitive, making it an excellent choice for beginners.
2. Extensive Documentation: Since Debian and Ubuntu are some of the most popular distributions, there is a wealth of documentation and resources available to troubleshoot issues and learn to use apt effectively. This significantly reduces the learning curve and helps resolve problems quickly.
3. Package Support: apt provides access to a vast number of packages in the official Debian and Ubuntu repositories. Additionally, the support for PPAs (Personal Package Archives) allows users to access newer software versions or programs that are not in the official repositories.
Disadvantages: Although apt is extremely reliable, it can be slower compared to other package managers like pacman, especially on systems with many pending updates.
dnf: El Poderoso Gestor de Fedora y Red Hat / dnf: The Powerful Manager of Fedora and Red Hat
Español: dnf es el sucesor de yum y es el gestor de paquetes predeterminado en Fedora, Red Hat y CentOS. Está diseñado para ser rápido y eficiente, con un enfoque en la resolución de dependencias y la gestión de transacciones de manera más inteligente.
1. Resolución Avanzada de Dependencias: Uno de los mayores puntos fuertes de dnf es su capacidad para manejar dependencias de manera avanzada. Cuando se instala un paquete, dnf garantiza que todas las dependencias necesarias se instalen correctamente, y también maneja la eliminación de dependencias obsoletas con el comando dnf autoremove.
2. Soporte para Módulos: dnf incluye soporte para módulos, una característica que permite a los usuarios instalar diferentes versiones de un mismo paquete o conjunto de paquetes, algo especialmente útil en entornos de desarrollo o servidores donde se necesita probar distintas versiones de software.
3. Gestión de Transacciones: dnf realiza un seguimiento de las transacciones de paquetes, permitiendo revertir cambios si algo sale mal durante una actualización o instalación. Esto agrega una capa extra de seguridad y estabilidad al sistema.
Desventajas: dnf tiende a ser más pesado y lento en comparación con apt y pacman. Además, aunque Fedora y Red Hat son populares, su comunidad no es tan amplia como la de Debian/Ubuntu, lo que puede hacer que la búsqueda de soluciones específicas sea más difícil.
English: dnf is the successor to yum and is the default package manager in Fedora, Red Hat, and CentOS. It’s designed to be fast and efficient, with a focus on smarter dependency resolution and transaction management.
1. Advanced Dependency Resolution: One of dnf’s greatest strengths is its ability to handle dependencies in an advanced manner. When a package is installed, dnf ensures that all necessary dependencies are installed correctly, and it also handles the removal of obsolete dependencies with the dnf autoremove command.
2. Module Support: dnf includes support for modules, a feature that allows users to install different versions of the same package or set of packages, which is especially useful in development environments or servers where different software versions need to be tested.
3. Transaction Management: dnf keeps track of package transactions, allowing you to roll back changes if something goes wrong during an update or installation. This adds an extra layer of security and stability to the system.
Disadvantages: dnf tends to be heavier and slower compared to apt and pacman. Additionally, although Fedora and Red Hat are popular, their community isn’t as large as Debian/Ubuntu’s, which can make finding specific solutions more challenging.
pacman: La Elección de los Entusiastas de Arch Linux / pacman: The Choice of Arch Linux Enthusiasts
Español: pacman es el gestor de paquetes utilizado por Arch Linux y sus derivadas, como Manjaro. Es conocido por su velocidad y simplicidad, alineándose con la filosofía de Arch de mantener las cosas simples, rápidas y eficientes.
1. Velocidad y Eficiencia: pacman es increíblemente rápido, tanto en la instalación como en la actualización de paquetes. Su diseño ligero permite realizar operaciones de gestión de paquetes con una rapidez notable, lo que lo hace ideal para usuarios avanzados que desean un sistema ágil y optimizado.
2. Control Total: pacman ofrece a los usuarios un control granular sobre la instalación y gestión de paquetes. Además, Arch Linux y pacman permiten una personalización extrema del sistema, dándole al usuario la capacidad de construir y optimizar su entorno desde cero.
3. Acceso al AUR (Arch User Repository): Uno de los grandes atractivos de pacman es su integración con el AUR, un repositorio comunitario donde los usuarios pueden encontrar y compartir paquetes que no están disponibles en los repositorios oficiales. Esto extiende enormemente las posibilidades de software disponibles para los usuarios de Arch.
Desventajas: pacman está diseñado para usuarios que tienen un nivel avanzado de conocimiento en Linux. Su curva de aprendizaje es empinada, y aunque es extremadamente poderoso, puede no ser la mejor opción para principiantes o usuarios que prefieren un sistema que funcione bien "out of the box".
English: pacman is the package manager used by Arch Linux and its derivatives, like Manjaro. It’s known for its speed and simplicity, aligning with Arch’s philosophy of keeping things simple, fast, and efficient.
1. Speed and Efficiency: pacman is incredibly fast, both in installing and updating packages. Its lightweight design allows for package management operations to be performed with remarkable speed, making it ideal for advanced users who want a fast and optimized system.
2. Full Control: pacman offers users granular control over package installation and management. Additionally, Arch Linux and pacman allow for extreme system customization, giving users the ability to build and optimize their environment from the ground up.
3. Access to the AUR (Arch User Repository): One of pacman’s major attractions is its integration with the AUR, a community repository where users can find and share packages not available in the official repositories. This greatly extends the software possibilities available to Arch users.
Disadvantages: pacman is designed for users with an advanced level of Linux knowledge. Its learning curve is steep, and while it is extremely powerful, it might not be the best option for beginners or users who prefer a system that works well "out of the box."
Conclusión / Conclusion
Español: La elección del gestor de paquetes ideal depende en gran medida de tus necesidades y nivel de experiencia. apt es excelente para usuarios que buscan estabilidad y facilidad de uso, dnf ofrece una gestión avanzada de dependencias y transacciones, ideal para entornos empresariales, mientras que pacman es la mejor opción para aquellos que buscan velocidad y control total sobre su sistema. Cada uno tiene sus fortalezas, y la decisión final debe basarse en lo que mejor se adapte a tu flujo de trabajo y preferencias.
English: The choice of the ideal package manager largely depends on your needs and experience level. apt is great for users seeking stability and ease of use, dnf offers advanced dependency and transaction management, ideal for enterprise environments, while pacman is the best choice for those looking for speed and full control over their system. Each has its strengths, and the final decision should be based on what best fits your workflow and preferences.
#Linux#PackageManagers#apt#dnf#pacman#LinuxComparisons#SoftwareManagement#Debian#Ubuntu#Fedora#ArchLinux#LinuxCommunity
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
does windowns 10 come with vpn
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
does windowns 10 come with vpn
Windows 10 VPN integration
Windows 10 VPN integration allows users to enhance their security and privacy while browsing the internet or accessing sensitive information over a network. By integrating a VPN (Virtual Private Network) into the Windows 10 operating system, users can establish a secure connection to another network over the internet, encrypting their data and protecting their online activities from being monitored or intercepted by unauthorized parties.
The VPN integration in Windows 10 provides users with the ability to connect to a remote server through a secure tunnel, ensuring that their online communications remain private and secure. This is especially useful when using public Wi-Fi networks, as it helps prevent hackers or malicious entities from intercepting sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, and personal data.
Moreover, Windows 10 VPN integration offers additional benefits such as bypassing geographical restrictions to access region-locked content, improving online anonymity by masking the user's IP address, and securing connections for remote workers accessing company resources.
Setting up a VPN in Windows 10 is relatively straightforward, with the operating system offering built-in support for various VPN protocols such as PPTP, L2TP/IPsec, SSTP, and IKEv2. Users can easily configure and manage their VPN connections through the Windows 10 settings menu, allowing for a seamless and hassle-free experience.
Overall, Windows 10 VPN integration provides users with a convenient and effective way to enhance their online security and privacy, ensuring a safer and more secure browsing experience in today's digital age.
Third-party VPN software compatibility
Third-party VPN software compatibility is a crucial consideration for users seeking to ensure seamless and secure browsing experiences. VPN (Virtual Private Network) services offer encryption and anonymity by routing internet traffic through a remote server. However, not all VPN software is compatible with every device or operating system, leading to potential limitations in functionality.
One of the primary factors impacting compatibility is the operating system of the device. While many VPN providers offer applications for popular platforms like Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android, compatibility with less common operating systems, such as Linux distributions or certain versions of mobile operating systems, may vary. Users should verify that their chosen VPN software supports their specific device or platform before installation.
Another aspect to consider is the level of integration with other software or applications. Some VPN providers offer dedicated apps or browser extensions that seamlessly integrate with popular web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, or Safari. This integration enhances user convenience by enabling one-click connection or automatic activation of the VPN when accessing specific websites or services.
Additionally, compatibility with streaming services and peer-to-peer (P2P) networks is essential for users who rely on VPNs for accessing geo-blocked content or torrenting securely. Not all VPN providers support access to streaming platforms like Netflix or Hulu, and some may restrict or throttle P2P traffic on their servers. Users should research and choose VPN software that explicitly mentions support for their desired streaming services or P2P activities.
Furthermore, compatibility with security protocols and encryption standards is crucial for ensuring data privacy and protection. Users should select VPN providers that offer robust encryption methods like AES-256 and support protocols such as OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPSec, or WireGuard for optimal security.
In conclusion, third-party VPN software compatibility encompasses various factors, including device and operating system support, integration with other software, compatibility with streaming services and P2P networks, and adherence to security protocols. By carefully assessing these aspects, users can choose VPN solutions that best meet their needs for privacy, security, and online accessibility.
VPN configuration options in Windows 10
When it comes to ensuring your online privacy and security, configuring a VPN on your Windows 10 device is essential. Windows 10 provides several options for setting up and customizing your VPN connection to meet your specific needs.
One of the most common methods to configure a VPN in Windows 10 is through the built-in VPN client. To set up a VPN connection, you can navigate to the Network & Internet settings and select the VPN tab. From there, you can add a new VPN connection by entering the necessary details such as the server address, type of VPN (e.g., PPTP, L2TP, SSTP, or IKEv2), and your login credentials.
Windows 10 also offers advanced VPN configuration options for users who require additional security features. You can access advanced settings by clicking on the "Advanced options" button while setting up a VPN connection. Here, you can configure DNS and proxy settings, set up split tunneling, enable automatic connection, and choose between different encryption protocols.
Moreover, Windows 10 allows users to customize their VPN connections further by accessing the Registry Editor. By making changes to the Windows Registry, you can tweak various VPN settings, such as maximum transmission unit (MTU) size, encryption algorithms, and connection timeouts.
In conclusion, Windows 10 provides flexibility and versatility when it comes to configuring a VPN connection. Whether you prefer using the standard settings or opting for advanced customization, Windows 10 offers a range of options to ensure a secure and private online experience through VPN technology.
Native VPN functionality in Windows 10
Windows 10, the widely used operating system by Microsoft, boasts native VPN functionality that provides users with the ability to establish secure connections over the internet. This built-in feature allows users to connect to VPN (Virtual Private Network) services without the need for additional software, offering convenience and accessibility in ensuring online privacy and security.
Setting up a VPN in Windows 10 is a straightforward process. Users can navigate to the Network & Internet settings, select VPN, and then add a new VPN connection by entering the necessary details provided by their VPN service provider. Windows 10 supports various VPN protocols, including PPTP, L2TP/IPsec, SSTP, and IKEv2, catering to different security and performance needs.
By utilizing the native VPN functionality in Windows 10, users can encrypt their internet traffic, mask their IP address, and access geo-restricted content with ease. Whether for enhancing privacy when browsing the web on public Wi-Fi networks or bypassing censorship while traveling abroad, a VPN in Windows 10 offers added layers of security and flexibility.
Moreover, Windows 10's VPN feature enables users to establish secure connections to their workplace networks remotely, fostering productivity and collaboration. With seamless integration into the operating system, users can enjoy a hassle-free VPN experience without the need to rely on third-party applications.
In conclusion, the native VPN functionality in Windows 10 empowers users to safeguard their online activities and enhance their internet experience. By leveraging this built-in feature, users can enjoy secure and private internet connections effortlessly, making Windows 10 a versatile platform for both personal and professional use.
VPN settings and features in Windows 10
VPN settings and features in Windows 10 provide users with a secure way to connect to the internet and protect their online privacy. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) encrypt data transmitted between the user's device and the internet, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential.
In Windows 10, setting up a VPN is a straightforward process. Users can access VPN settings by going to the Network & Internet section in the Settings menu. From there, they can choose to add a new VPN connection and enter the necessary details provided by their VPN service provider, such as the server address, type of VPN (e.g., IKEv2, L2TP/IPsec, PPTP), and login credentials.
Windows 10 offers various features to enhance the VPN experience. One such feature is the ability to automatically connect to the VPN when using specific networks or apps, ensuring that the connection is always secure. Additionally, users can select whether to allow or block VPN connections for individual apps, giving them more control over their online security.
Furthermore, Windows 10 provides built-in support for VPN protocols like IKEv2 and SSTP, making it easy for users to configure their VPN connections without the need for third-party software. This ensures a seamless and secure browsing experience while using a VPN on Windows 10.
Overall, the VPN settings and features in Windows 10 play a vital role in safeguarding users' online activities and protecting their data from potential threats. By utilizing these tools effectively, users can browse the internet with peace of mind knowing that their privacy is being prioritized.
0 notes
Text
"Astral Ascent" finaliza su Early Access el 14 de noviembre
El estudio francés @HibernianWS anunció que "Astral Ascent" se lanzará oficialmente el 14 de noviembre del 2023.
El estudio francés Hibernian Workshop anunció hoy que Astral Ascent se lanzará oficialmente el 14 de noviembre de 2023 para PC/Mac/Linux a través de Steam, en PS5/PS4 (PlayStation Store), y en Nintendo Switch (eShop). Este desafiante rogue-lite ha estado en Early Access desde abril del año pasado, y recibirá su actualización 1.0 con nuevo contenido y añadidos y mejoras demandadas por la…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
"¡Prepárate para Luchar por tu Vida! 'REMEDIUM', el Adrenalínico Shooter de Doble Palanca, Lanza su Ofensiva en PC el 14 de Septiembre
Prepárate para adentrarte en el sombrío Renacimiento postapocalíptico de REMEDIUM, el emocionante shooter de doble palanca desarrollado por Sobaka Studio y publicado por ESDigital Games. ¡La primera y mortífera entrega del juego estará disponible en PC a través de Steam Early Access y Epic Games Store para Windows, Mac y Linux el jueves 14 de septiembre de 2023, con una segunda y tercera entrega…

View On WordPress
#acción rápida#alquimia#demo de juegos#emoción y diversión#jefes desafiantes#paisajes desolados#postapocalipsis#supervivencia
0 notes
Link
#command#CommandOptionswhoami#CommandOptionswhoamiCommand#CommandSyntaxwhoami#CommandSyntaxwhoamiCommand#commands#Commandswhoamivs.wwhoami#ContentswhoamiCommand#ContentswhoamiCommandSyntaxwhoami#Effective#effectiveuser#help#helpful#Linux#Linuxcommands#OptionswhoamiCommand#OptionswhoamiCommandExamplesBasic#sudo#SyntaxwhoamiCommand#SyntaxwhoamiCommandOptionswhoami#user#users#vs#whoami#whoamicommand#whoamiLinuxCommand
1 note
·
View note